If I had to guess, the Russian Army did not think it was going to be in Ukraine very long.
The following is a man in-depth assessment of how badly the Russian telecoms system has failed its military. It is a mash-up of work done by Bellingcat, the OSINT team at Reuters, OSINT-Technical, Russian military expert Vladimir Orlov, and Russian investigative journalists Sergei Dobrynin and Mark Krutov.
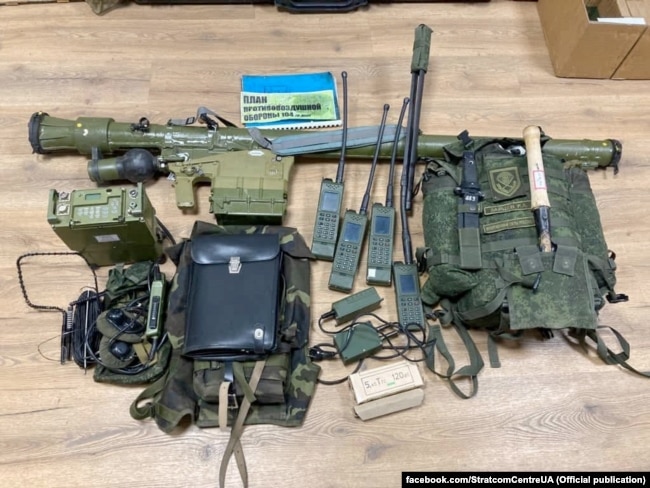 ABOVE: Russian equipment, including Azart radios, captured during the fighting in Ukraine
ABOVE: Russian equipment, including Azart radios, captured during the fighting in Ukraine
30 March 2022 – Typical of material you’ll find across Youtube and TikTok. A bedraggled Russian soldier tells his interrogators in a video:
“We have no communication. We have no walkie-talkies. Nothing. We were not going to be here long they told us”.
This was a mere two weeks into the war, and such statements, along with scores of intercepted chatter, captured equipment, and images of cheap, handheld transceivers, suggested that an inability to communicate – up and down the chain of command and across branches of the Russian military – would impede Moscow’s war plans. And while military fortunes can swing quickly, in even major offensives like the one launched by Russian President Vladimir Putin on 24 February 24 to “demilitarize” and subdue Ukraine, many Western military experts suggest that the Kremlin and its planners botched key aspects of the early weeks of the invasion as I have highlighted in this series.
In Russia’s case, the predicament has been on display over the first 24 days of this war through statements by captive troops, tapped conversations, and other clues posted by Ukrainian intelligence or others eager to highlight perceived weaknesses in the much larger invading forces, and reports suggesting an unsecured call might have aided Ukrainian forces in targeting at least one of seven Russian generals who have reportedly been killed in the conflict. Evidence suggests that some of the roots of the Russian communication lapses lie in mismanaged development and procurement processes for things like tactical military radios, undertrained and under-deployed specialists, and the challenges of operating on foreign soil, where the enemy controls not only cellular networks but also wired communications that frequently serve as a reliable backup channel.
One of the results has been varying complexity among the systems used by troops for voice and data communications, multiplying challenges particularly because they involve mixed air, land, and naval forces. In such cases, all troops are forced to use a system that’s common to the least advanced among them. Stanimir Dobrev, an independent military expert who specializes in telecommunications:
“If you’re forming a mixed formation and part of the formation is comprised of older vehicles like the 90th Guards Tank Division approach into Kyiv we saw recently, you have to resort to the lowest common denominator”.
In other words, mixing so-called open and encrypted systems makes them only as strong as their weakest link. Some of those Russian forces’ older equipment, Dobrev said, “can be decrypted almost in real time and thus it’s not useful to add the extra layer of complexity to operate the equipment when there’s little benefit.”
Those and other factors potentially point to why Russia’s ground offensive has bogged down, and air operations become less effective over time, as targets identified and communicated to Russia’s air force early on have moved.
But Russia has been here before. It’s five-day war in Georgia in August 2008, over two breakaway Georgian regions Moscow has since occupied, laid bare some of the Russian armed forces’ most pressing battleground problems: tactical communications. Some units were unable to communicate with the command structure. Mobile phones and even sending a courier up the line like during World War I were used instead of military radios. And in one extreme example, an air force officer flew by helicopter to hand out orders personally. A deputy chief of the Russian General Staff, Yevgeny Meychik, responded in 2009 with an announcement that, under orders from Russia’s then-president, Dmitry Medvedev, the Defense Ministry would thoroughly revise its approach to the military command-and-control system — “and particularly the communications systems.” He pledged that “by the end of 2011, we plan to bring a radio station to every serviceman, to every combat vehicle.”
But while Meychik’s plan presupposed use of the main tactical-level army radio system at the time, known as Akveduk, the Defense Ministry instead opted to pursue the development of a wholly new, sixth-generation system that came to be known as Azart. An upstart manufacturer, Angstrem, one of whose owners had been an adviser to Medvedev, was chosen for the project (“paging Boris Johnson”). By early 2012, boasting that Russia had employed the NATO concept of “lessons learned,” Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin appeared with one of the Azart handsets and declared, “This connection works!”
Years of promises and many unmet deadlines to deliver the phones, dubbed “green crocodiles” by troops because of their half-meter-long antennas, followed, their use at the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics notwithstanding. Thirteen years later, despite more repeated promises, thousands of the Azart phones are in the hands of Russian troops. But it is hard to describe the process as a success. It has been the subject of multiple criminal investigations, including an ongoing one focused on a deputy chief of the Russian General Staff, Colonel General Khalil Arslanov.
NOTE: reviews on radio forums like Radioscanner.ru, while impossible to independently corroborate, appear to suggest the Azarts are unpopular among troops. Military expert Vladimir Orlov described the use of Azart phones among Russian troops deployed to Syria and said that “outside the bases of the Russian armed forces in Syria, everyone uses mobile phones and Chinese ‘balalaikas,'” a reference to civilian walkie-talkies manufactured by China’s Baofeng.
ABOVE: an Azart military radio on sale in Russia, apparently by a member of the Russian Army
Moreover, the most generous estimate of the total number of Azart handsets deployed is only around 60,000, based on the 18 billion rubles ($171 million at the current rate) allocated for their purchase and the estimated cost of around 300,000 rubles per device. That is only around one-third the number of Russian troops thought by NATO and Ukraine to have been deployed in Ukraine.
The inevitable knock-on problems
Analyst Dobrev points to the Russian military’s failure to ensure modern and secure communication channels as a major stumbling block. But he emphasizes the importance of the knock-on effect of such a problem – poor coordination among the various ground, sea, and air forces involved in the full-scale invasion of Ukraine.And he says that the Russian military’s failure to implement a modern, automated command-and-control system is another problem:
“By 2020, it was planned to equip just 45 brigades of the Russian ground forces with such a system, but Russia hasn’t managed the task. The situation is even worse with the coordination between ground forces and the air force which operates on its own command-and-control system. The resulting problems in coordination present another problem, that seems to have manifested itself as the war ground on. At the beginning of the war, the Russian Air Force acted quite successfully because the positions of the enemy were known to it. Now this doesn’t always work”.
He pointed to leaked documents and OSINT acquired documents that appear to show the Russian Air Force operating by making sorties to designated targets with little or no ability to communicate with ground forces who, for instance, might otherwise request a change of targets or air support. Dobrev also says that forward detachments in the early days of the war appeared to have outrun their communications support:
“The Russian battalion tactical groups immediately went a much greater distance from the border, and at the same time, we didn’t see equipment that could provide secure communication with the command post along with them”.
And therein lies the problem. Repeater cars and new communication towers need to be installed along the way, and their set-up and use require experienced operators. Indirectly, this indicates that the Russian offensive groups didn’t expect to stay on the road for a long time. Clear signs have emerged of interception of communication between Russian special services and other troops that should otherwise be on encrypted channels.
Moreover, Christo Grozev, of the open-source sleuthing group Bellingcat, has cited on Twitter in numerous posts (here is just one) that the “super expensive cryptophone system” introduced by Russia in 2021 is seemingly being intercepted because it requires a 3G or 4G cellular network to operate. The cellular networks are still controlled by Ukraine, which means that for the Ukrainian military they remain a relatively secure means of communication from eavesdropping. Not so for Russians using those same networks, or, obviously, Ukrainian fixed lines. In the absence of special, secure army communications, many soldiers and officers succumb to the temptation to use ordinary phones. They simply take out Ukrainian SIM cards and call Russia, allowing the Ukrainian military and intelligence not only to easily intercept the content of the conversations, but also to determine the location of the caller.
NOTE: this ties into the article in my series on why Ukrainian snipers are having an easier time knocking off generals. Many Russian generals talk on unsecured phones and radios, and in at least one case Ukrainians geolocated a call and killed him in an attack on his location.
The BBC reported in the first days of the war that audio messages purportedly including Chechen head Ramzan Kadyrov suggested that a commander in his guards corps was traveling to Moscow on the eve of the war to obtain “clean Ukrainian SIM cards,” presumably leaving communications with those devices vulnerable to Ukrainian high-tech eavesdropping.
Military communications

Communication technology is evolving rapidly, changing the way military forces communicate but also creating new threats. I cannot explore everything in this post so just a few thoughts on military communications networks and technology which I learned doing this series, as well as what I have learned during multiple trips to the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, Spain and the International Cybersecurity Conference in Lille, France.
The global tactical military communications market, which comprises airborne, naval, man-portable, vehicular and stationary, is set to see substantial growth over the coming decade. According to market analysis by GlobalData in its 2021 report, by the end of 2028, the sector will be worth $151bn globally. This growth is driven largely by demand for man-portable innovations, which account for more than a third of the market (38%).
The modernisation of man-portable communications systems in particular has long been on the wish lists of armies relying on traditional radio in the field. The US Army, for instance, has been looking to modernise its tactical military communications infrastructure for more than 20 years, starting with the joint tactical radio system (JTRS) in 1997. The basic idea was to field a family of radios and waveforms that could be modified by downloading new software rather than replacing expensive hardware. Software reconfigurability supposedly would enable a patchwork of disparate networks to communicate as if everyone was using an iPhone, even in the midst of combat.
What if everyone was using an iPhone, though? Experience with smartphones in the military has shown that they can compromise security through features such as geo-location services, which is why the US Army has reportedly prohibited its service personnel from using those services in operational environments. Smartphones can pose significant security risks for an individual, a squadron and ultimately an operation in a military setting, but they haven’t been written off altogether. As one U.S. military advisor told me , when it comes to communicating on the battlefields of tomorrow … everybody in the army seems to agree on what they would like. It’s an iPhone.
Integrating 5G into the defence infrastructure
Meanwhile, the introduction of 5G networks is gathering pace, opening up a new era of possibilities – and threats – for military communications. Like the roads and skies of the world, communication channels are increasingly populated. Although 5G is the next generation of mobile communications intended to address that, it also means there will be more capacity and therefore greater demand. While 5Gt offers potential unlike anything before it within the military domain, undoubtedly the biggest single threat it brings is jamming and signal interception. Man-portable radio is set to be the stand-out beneficiary, with the prospect of communications even in the world’s hardest-to-reach environments with the expanded and enhanced spectrum it boasts. However, with increased capability and capacity comes the obvious test: will it be possible for the military to utilise the network to its full potential given the growing data appetite of the commercial sector? That remains to be seen.
The data war
The battle for data supremacy has already gained pace, and the roll-out of 5G will revolutionise military communications, raising the stakes between those developing the technology, and ultimately change the warfare and cybersecurity landscape.
It seems that, since the days of the Iraqi insurgency and Afghanistan conflict, the attention of the world’s militaries and those leading them is shifting back to the more conventional image of war – state on state conflict. Command and control has arguably never been more important, or challenging. Communications has always been the defining factor of conflict, but never more so than today. How countries respond to that challenge will be the determining factor in global influence.